CNC Machining Methods: Milling vs. Turning – Key Differences and Applications
AUTHOR: Creallo Marketing Team|2025.08.12
What is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computerized Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process that uses automated machine tools controlled by programmed numerical code.
By precisely cutting and shaping materials such as metals, plastics, and engineering composites, CNC machining delivers accurate, repeatable parts for industries including automotive, electronics, aerospace, and industrial equipment. Using a CNC machine, manufacturers can produce complex geometries directly from 3D CAD files, ensuring tight tolerances and consistent quality even in high-volume production.
In this guide, we compare two of the most widely used CNC machining processes — milling and turning — including their features, strengths, and limitations.

1. CNC Milling
CNC milling uses a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a stationary workpiece. It’s ideal for producing flat, contoured, and complex surfaces, and is widely used for automotive parts, mold components, and precision mechanical assemblies.
Capabilities by Axis Count
- 3-axis – Efficient for simple geometries
- 4-axis – Enables machining on multiple faces without repositioning
- 5-axis – Ideal for intricate, multi-surface geometries with fewer setups
Advantages:
- High dimensional accuracy and repeatability
- Flexible for a variety of shapes and sizes
Limitations:
- Tool access can restrict certain geometries
- May require multiple setups for deep or enclosed features
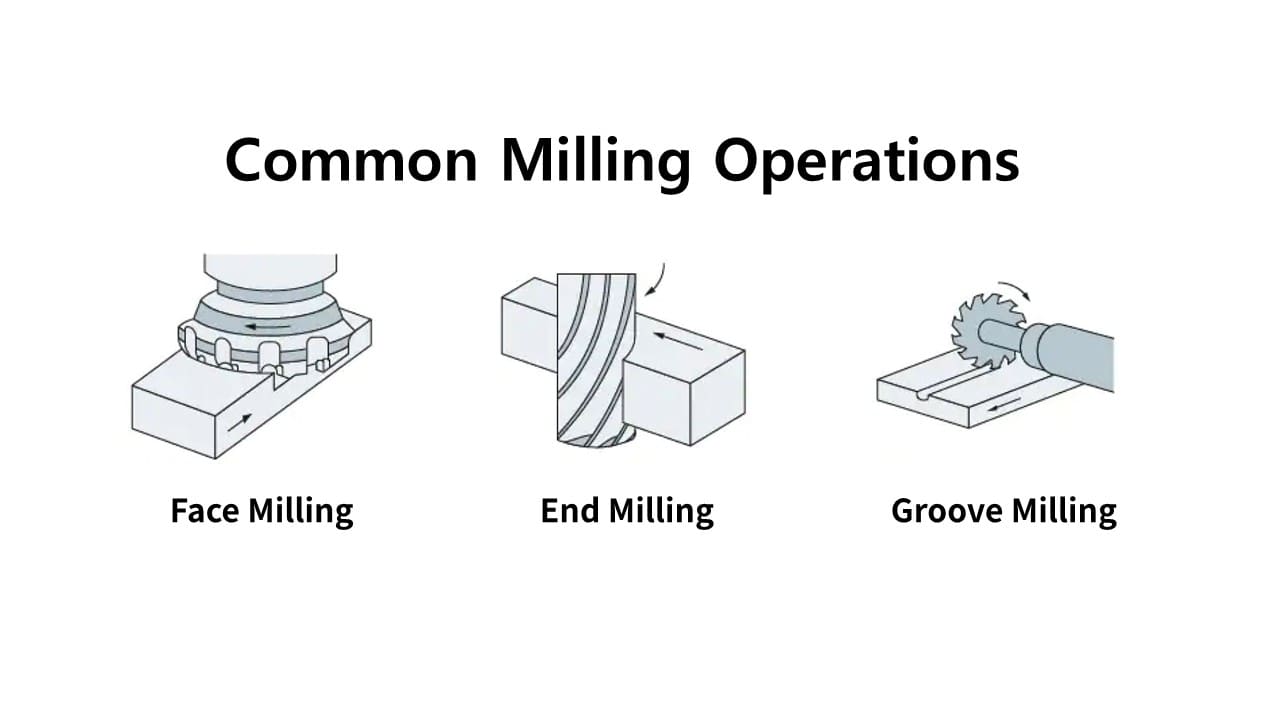
Common Milling Operations
- Face Milling – Creates flat, high-precision surfaces using a multi-edge cutter; ideal for large surface removal.
- End Milling – Produces detailed features such as pockets, slots, and contours with a slender, drill-like cutter.
- Groove Milling – Cuts uniform-width channels, often used for keyways or assembly slots.

2. CNC Turning
CNC turning (or lathe machining) rotates the workpiece while a stationary cutting tool removes material. It’s the go-to process for cylindrical parts such as shafts, pins, and threaded components.
Advantages:
- Fast cycle times and high productivity
- Lower per-unit cost for cylindrical parts
Limitations:
- Limited to rotationally symmetric geometries
- Complex features may require secondary machining
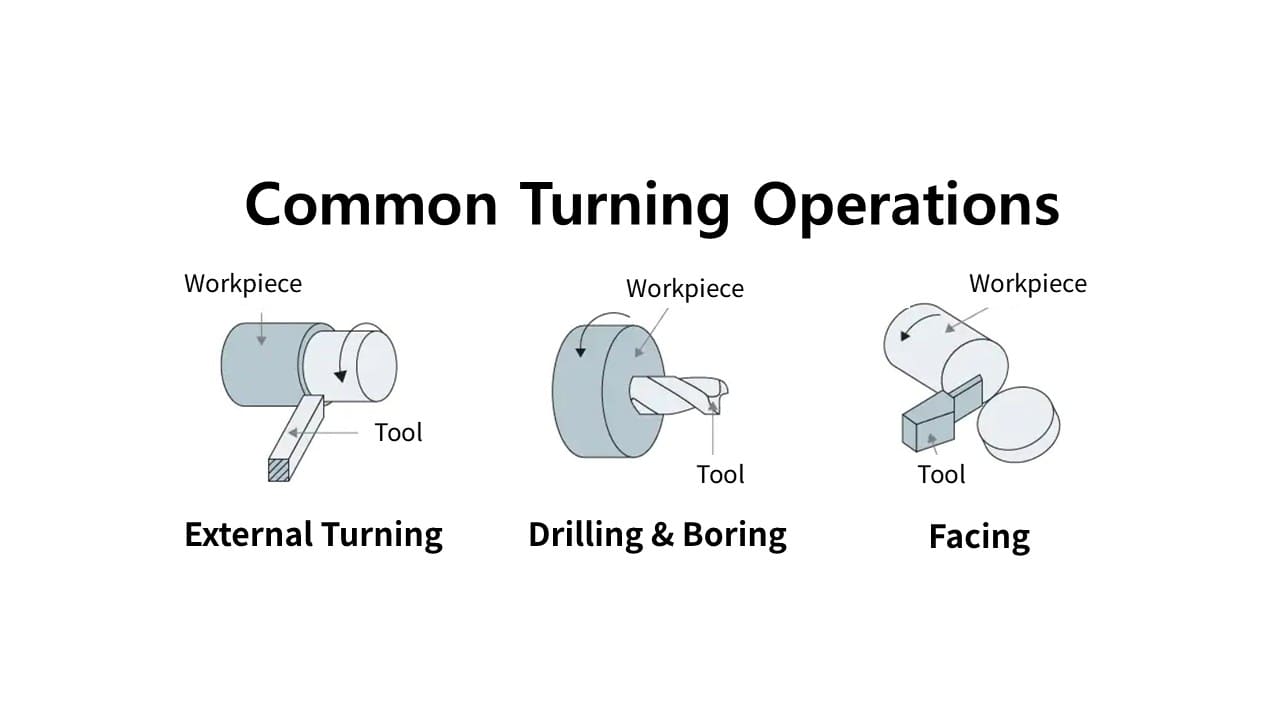
Common Turning Operations
- External Turning – Shapes the outside diameter of parts.
- Drilling & Boring – Creates or enlarges holes; boring improves internal diameter precision.
- Facing – Flattens the end surface for assembly or sealing applications.

AI-Powered CNC Machining with Creallo
Creallo’s AI-driven design analysis instantly determines whether milling or turning is the best fit for your part. Simply upload your 3D CAD file to:
- Get instant manufacturability feedback
- Receive an accurate quote and lead time in minutes
- Place your order online — no lengthy supplier search required
We offer:
- In-house production in Korea for urgent orders
- Verified global manufacturing network for cost efficiency and scalability
- Full range of materials and finishing options to meet your application needs
Experience fast, reliable, and cost-effective CNC machining — from prototype to production — all in one platform.
Explore CNC Materials →
Learn More About Creallo CNC Machining Services →




